Description of Work Packages
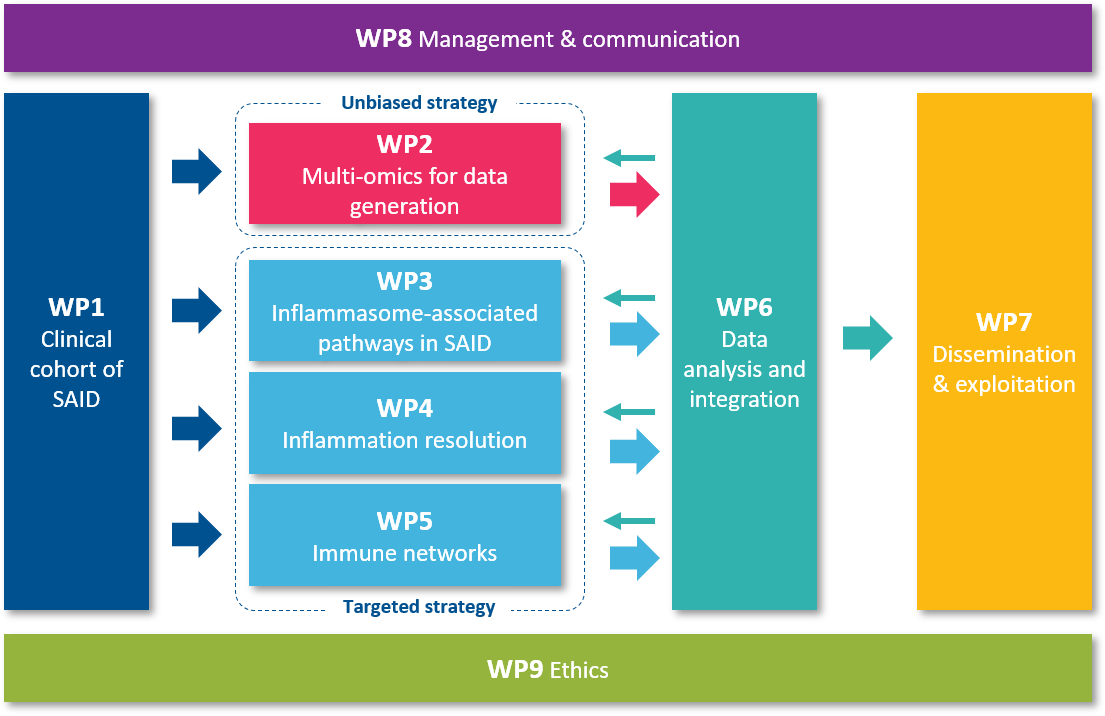
 Clinical cohort
Clinical cohort
Systemic Autoinflammatory Disorders (SAID) are a set of rare diseases and, as such, building a cohort requires the involvement of a significant number of clinical centres. Multiplying the recruiting sites and operating at the pan-European level increases the complexity of the regulatory and logistical dimensions of the study.
The objective is to establish a large collection of samples and associated clinical data from undiagnosed SAID patients (and their parents), monogenic SAID patients and healthy donors follow a rigorously identical process, as a pre-requisite for further biological and computational analyses.
 Multi-omics
Multi-omics
Multi-omics is a biological analysis approach for gathering and combining data on multiple “omes”. From the samples collected from SAID patients, ImmunAID will investigate:
- The genome, using a genome-wide approach, based on next generation sequencing analysis, aimed at discovering novel genetic variants.See the explaining video.
- The transcriptome, using miRNA analysis aimed at identifying unique mRNA & miRNA profiles in immune cells. See the explaining video.
- The proteome, using mass spectrometry and multiplexed proteomic analyses aimed at pinpointing disease-specific new protein biomarkers in plasma. See the explaining video.
- The microbiome, using shotgun metagenomics aimed at detecting phylogenetic or functional biomarkers.See the explaining video.
Omics being non-targeted approaches, the objective is to identify new mechanisms of pathogenesis, which could be turned into new disease biomarkers and targets for intervention.
 Inflammasome-associated pathways
Inflammasome-associated pathways
Inflammasomes are multi-molecular platforms triggered by the innate immune system and are responsible for the activation of inflammatory responses. Although inflammasomes may play a key role in the onset of autoinflammatory disorders, knowledge on both upstream (how are they formed?) and downstream (which processes they trigger?) pathways is still scarce.
The main objective is thus to assess the range of functions, dysfunction and biomarker potential of the inflammasome complexes in SAID.
By correlating with omics data from WP2 we will seek to further ascertain inflammasome-associated signatures.
 Inflammation resolution
Inflammation resolution
Termination of inflammation is now considered as an active and highly orchestrated process of similar importance and complexity to the onset and progression of inflammation. It is called resolution and involves the induction of a network of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), whose role is to smoothly terminate all the inflammation processes.
Autoinflammatory diseases, being characterized by prolonged, persistent and/or recurrent inflammatory reactions, might involve impaired resolution.
The goal is to characterize SPM networks, biosynthetic pathways and functional effects in SAID patients and identify potential abnormalities in the resolution process.
 Immune networks
Immune networks
For most autoinflammatory disorders, the stimuli that initiate and/or propagate the inflammatory and immune responses are not fully identified.
The objective is to first gain knowledge on individual inflammation factors through the profiling of soluble factors (e.g. cytokines, alarmins) and specific immune cells (e.g. NK cells, Tregs) and the characterisation of protein structures and modifications. The generated data will then be integrated into a network view, with a strong emphasis on mutual interactions, and cross-regulation.
Omics data from WP2 may further help to uncover novel players and signatures related to immune networks.
 Data analysis and integration
Data analysis and integration
The large amount of biological data that will be generated throughout WP2 to WP5 will be managed centrally, further analysed, and integrated with the clinical datasets collected in WP1.
Both clinical and biological datasets will be exploited to identify clinically meaningful classes of SAID patients. Diagnostic classifications will be developed for their prognostic and therapeutic potential.
The latest methodologies in bioinformatics, statistical modelling, machine learning, and deep learning will be applied to the ImmunAID datasets. Supervised and unsupervised approaches, as well as knowledge-driven approaches, will be combined to optimize the classification approach, keeping a strong link to biological mechanisms and clinical impact.
 Dissemination and exploitation
Dissemination and exploitation
What is done with the data and the results generated by the project will be key to making an impact on SAID science and patients’ life. The objective is to turn research results into reliable and marketable diagnostic tools, usable and affordable for physicians.
For that purpose, intellectual property protection will be sought where necessary to enable further exploitation. Advice from expert stakeholders will also be sought to ensure that both regulatory and industrial process issues are being properly considered. Broad dissemination of scientific results will be encouraged to stimulate the field of autoinflammatory science and ensure sustainability of the project’s achievements.
 Management and communication
Management and communication
Rigorous management procedures will be setup to help steer project advances, anticipate risks and ensure the achievement of the project’s objectives. Special attention will be given to integrate the latest results from the broad scientific community in adapting the project’s scientific strategy.
Effective communication will also be organised to reach out to a broad panel of stakeholders spanning from the research community, patients, and patient associations to guideline- and policy-forming bodies.



