MKD*
| Epidemiology | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Gender ratio |
1 : 1 |
Prevalence |
>300 cases |
Disease presentation
Genetic grounds
The disease shows an autosomal recessive inheritance (i.e., each parent must give a mutated gene for a child to develop the disease). The involved mutated gene is MVK coding for mevalonate kinase involved in cholesterol synthesis.Main clinical symptoms
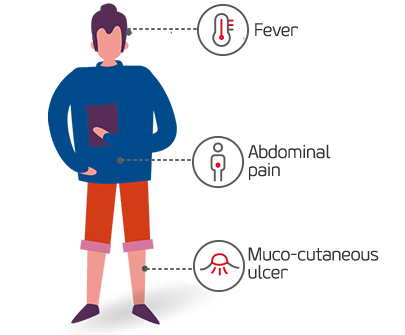
 Elevated fever with chills
Elevated fever with chills
 Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
 Mouth ulcers
Mouth ulcers
Biological signs
 Increase of C-reactive protein (CRP)
Increase of C-reactive protein (CRP)
 Decrease of mevalonate
Decrease of mevalonate
Therapy
- Anti-IL-1 (e.g. Anakinra, Canakinumab)
- Corticosteroids
- Anti-IL-6 (e.g. Tocitizumab)
*Mevalonate Kinase Disease, also known as Hyper-IgD syndrome (HIDS)





